दूरी-सूत्र: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(content added) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
निर्देशांक ज्यामिति में दूरी सूत्र का उपयोग <math>XY | |||
</math> | </math> समतल में दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने के लिए किया जाता है। <math>y- | ||
</math> | </math>अक्ष से किसी बिंदु की दूरी को उसका <math>x- | ||
</math> | </math>निर्देशांक या भुज कहते हैं। <math>x- | ||
</math> | </math>अक्ष से किसी बिंदु की दूरी को उसका <math>y- | ||
</math> | </math>निर्देशांक या कोटि कहते हैं। <math>x- | ||
</math> | </math>अक्ष पर किसी बिंदु के निर्देशांक <math>(x,0) | ||
</math>, | </math> के रूप के होते हैं, और <math>y- | ||
</math> | </math>अक्ष पर किसी बिंदु के निर्देशांक <math>(0,y)</math> के रूप के होते हैं। किसी समतल में किसी भी दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने के लिए, हम पाइथागोरस प्रमेय का उपयोग करेंगे। | ||
</math> | |||
== | == दूरी-सूत्र क्या है? == | ||
दूरी सूत्र वह सूत्र है, जिसका उपयोग किसी भी दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने के लिए किया जाता है, केवल तभी जब निर्देशांक हमें ज्ञात हों। ये निर्देशांक <math>x- | |||
</math> | </math>अक्ष या <math>y- | ||
</math> | </math>अक्ष या दोनों पर स्थित हो सकते हैं। मान लीजिए, एक <math>XY | ||
</math> | </math> समतल में दो बिंदु, मान लीजिए <math>A | ||
</math> | </math> और <math>B | ||
</math> | </math> हैं (चित्र-1 देखें) बिंदु <math>A | ||
</math> | </math> के निर्देशांक <math>(x_1,y_1) | ||
</math> | </math> हैं और <math>B | ||
</math> | </math> के <math>(x_2,y_2) | ||
</math> | </math> हैं। | ||
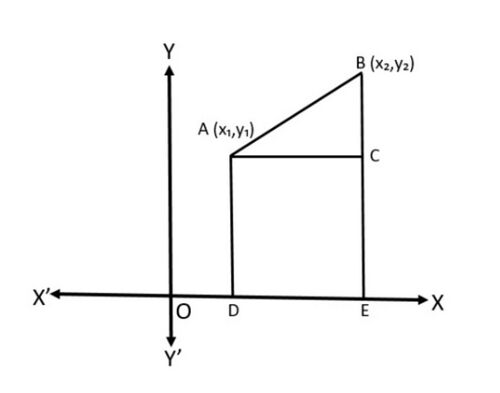
[[File:Distance Formula.jpg|alt=Fig 1 - Distance Formula|none|thumb|500x500px| | [[File:Distance Formula.jpg|alt=Fig 1 - Distance Formula|none|thumb|500x500px|चित्र-1- दूरी-सूत्र]] | ||
फिर दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने का सूत्र <math>AB</math> द्वारा दिया गया है | |||
</math> | |||
<math>AB=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2 } | <math>AB=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2 } | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
== | == दूरी-सूत्र व्युत्पत्ति == | ||
आइए चित्र-1 में दर्शाए गए दो बिंदुओं <math>A(x_1,y_1) | |||
</math> | </math> और <math>B(x_2,y_2) | ||
</math> | </math> के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करें | ||
<math>x- | |||
</math> | </math>अक्ष पर लंबवत <math>AD | ||
</math> | </math> और <math>BE | ||
</math> | </math> खींचिए। <math>BE | ||
</math> | </math> पर बिंदु <math>A | ||
</math> | </math> से एक लंबवत बिंदु <math>C | ||
</math> | </math> पर मिलने के लिए खींचा जाता है। | ||
तो, <math>OD=x_1 | |||
</math> , <math>OE=x_2 | </math>, <math>OE=x_2 | ||
</math> | </math> तो <math>DE=x_2-x_1=AC | ||
</math> | </math> । साथ ही C<math>EB=y_2 | ||
</math> , <math>EC=AD=y_1 | </math>, <math>EC=AD=y_1 | ||
</math>. | </math>. इसलिए <math>BC=y_2-y_1 | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
अब, पाइथागोरस प्रमेय को <math>\bigtriangleup ACB </math> में लागू करते हुए , हम पाते हैं | |||
<math>AB^2=AC^2+BC^2 | <math>AB^2=AC^2+BC^2 | ||
| Line 58: | Line 56: | ||
<math>AB=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} | <math>AB=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} | ||
</math> | </math> दूरी-सूत्र है। | ||
=== | === उदाहरण === | ||
दोनों बिंदुओं <math>A(1,2) | |||
</math> | </math> और <math>B(3,4) | ||
</math> | </math> के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात कीजिए | ||
''' | '''हल:''' | ||
मान लीजिए <math>A(1,2)=(x_1,y_1) | |||
</math> | </math> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 73: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
दो बिंदुओं <math>A | |||
</math> | </math> और <math>B | ||
</math> | </math> के बीच की दूरी | ||
<math>AB=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} | <math>AB=\sqrt{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:55, 19 June 2024
निर्देशांक ज्यामिति में दूरी सूत्र का उपयोग समतल में दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने के लिए किया जाता है। अक्ष से किसी बिंदु की दूरी को उसका निर्देशांक या भुज कहते हैं। अक्ष से किसी बिंदु की दूरी को उसका निर्देशांक या कोटि कहते हैं। अक्ष पर किसी बिंदु के निर्देशांक के रूप के होते हैं, और अक्ष पर किसी बिंदु के निर्देशांक के रूप के होते हैं। किसी समतल में किसी भी दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने के लिए, हम पाइथागोरस प्रमेय का उपयोग करेंगे।
दूरी-सूत्र क्या है?
दूरी सूत्र वह सूत्र है, जिसका उपयोग किसी भी दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने के लिए किया जाता है, केवल तभी जब निर्देशांक हमें ज्ञात हों। ये निर्देशांक अक्ष या अक्ष या दोनों पर स्थित हो सकते हैं। मान लीजिए, एक समतल में दो बिंदु, मान लीजिए और हैं (चित्र-1 देखें) बिंदु के निर्देशांक हैं और के हैं।
फिर दो बिंदुओं के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करने का सूत्र द्वारा दिया गया है
दूरी-सूत्र व्युत्पत्ति
आइए चित्र-1 में दर्शाए गए दो बिंदुओं और के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करें
अक्ष पर लंबवत और खींचिए। पर बिंदु से एक लंबवत बिंदु पर मिलने के लिए खींचा जाता है।
तो, , तो । साथ ही C, . इसलिए
अब, पाइथागोरस प्रमेय को में लागू करते हुए , हम पाते हैं
दूरी-सूत्र है।
उदाहरण
दोनों बिंदुओं और के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात कीजिए
हल:
मान लीजिए
दो बिंदुओं और के बीच की दूरी