लम्ब वृत्तीय शंकु का आयतन: Difference between revisions
From Vidyalayawiki
No edit summary |
(added content) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Right Circular Cone.jpg|thumb|150x150px]] | [[File:Right Circular Cone.jpg|thumb|150x150px]] | ||
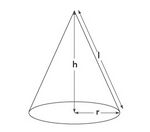
शंकु का आयतन शंकु की जगह या क्षमता को परिभाषित करता है। शंकु एक त्रि-आयामी ज्यामितीय आकृति है जिसमें एक गोलाकार आधार होता है जो एक वृत्तीय आधार से एक बिंदु तक सपाट होता है जिसे कोणबिंदु या शीर्ष कहा जाता है। एक शंकु रेखा खंडों, अर्ध-रेखाओं या रेखाओं के एक समूह द्वारा बनता है जो एक सामान्य बिंदु, शीर्ष को आधार पर सभी बिंदुओं से जोड़ता है जो एक ऐसे तल में होता है जिसमें शीर्ष नहीं होता है। | |||
शंकु को गैर-सर्वांगसम गोलाकार डिस्क के एक समुच्चय के रूप में देखा जा सकता है जो एक दूसरे पर इस तरह से ढेर होते हैं कि आसन्न डिस्क की त्रिज्या का अनुपात स्थिर रहता है। | |||
शंकु का आयतन = <math>\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h</math> | |||
जहाँ <math>r</math> आधार त्रिज्या है और <math>h</math> शंकु की ऊँचाई है। | |||
== | == उदाहरण == | ||
1. | 1.एक शंकु की ऊंचाई और तिर्यक ऊंचाई क्रमशः <math>21</math> cm और <math>28</math> cm है। | ||
शंकु का आयतन ज्ञात कीजिए। | |||
हल: | |||
<math>l^2=r^2+h^2</math> से | |||
<math>r=\sqrt{l^2 -h^2}</math> | <math>r=\sqrt{l^2 -h^2}</math> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<math>r=\sqrt{28^2 -21^2}=\sqrt{784 -441}=\sqrt{343}=\sqrt{49 \times 7}=7\sqrt{7}</math> cm | <math>r=\sqrt{28^2 -21^2}=\sqrt{784 -441}=\sqrt{343}=\sqrt{49 \times 7}=7\sqrt{7}</math> cm | ||
शंकु का आयतन = <math>\frac{1}{3}\pi r^2 h</math> | |||
=<math>\frac{1}{3}\times \frac{22}{7}\times (7\sqrt{7})^2 \times 21=7546</math> cm<sup>3</sup> | =<math>\frac{1}{3}\times \frac{22}{7}\times (7\sqrt{7})^2 \times 21=7546</math> cm<sup>3</sup> | ||
[[Category:पृष्ठीय क्षेत्रफल और आयतन]][[Category:कक्षा-9]][[Category:गणित]] | [[Category:पृष्ठीय क्षेत्रफल और आयतन]][[Category:कक्षा-9]][[Category:गणित]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:09, 10 September 2024
शंकु का आयतन शंकु की जगह या क्षमता को परिभाषित करता है। शंकु एक त्रि-आयामी ज्यामितीय आकृति है जिसमें एक गोलाकार आधार होता है जो एक वृत्तीय आधार से एक बिंदु तक सपाट होता है जिसे कोणबिंदु या शीर्ष कहा जाता है। एक शंकु रेखा खंडों, अर्ध-रेखाओं या रेखाओं के एक समूह द्वारा बनता है जो एक सामान्य बिंदु, शीर्ष को आधार पर सभी बिंदुओं से जोड़ता है जो एक ऐसे तल में होता है जिसमें शीर्ष नहीं होता है।
शंकु को गैर-सर्वांगसम गोलाकार डिस्क के एक समुच्चय के रूप में देखा जा सकता है जो एक दूसरे पर इस तरह से ढेर होते हैं कि आसन्न डिस्क की त्रिज्या का अनुपात स्थिर रहता है।
शंकु का आयतन =
जहाँ आधार त्रिज्या है और शंकु की ऊँचाई है।
उदाहरण
1.एक शंकु की ऊंचाई और तिर्यक ऊंचाई क्रमशः cm और cm है।
शंकु का आयतन ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल:
से
cm
शंकु का आयतन =
= cm3