वृत्त की स्पर्श रेखा: Difference between revisions
(New Page Created) |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | A circle is a set of all points in a plane which are equally spaced from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the center of the circle and the distance between any point on the circle and its center is called the radius. | ||
[[ | |||
[[Category:वृत्त]] | == Definition == | ||
A tangent to a circle is a line which intersects the circle at only one point. The common point between the tangent and the circle are called the point of contact. | |||
Given, a line to a circle could either be intersecting, non-intersecting or just touching the circle. | |||
Consider any line <math>AB</math> and a circle. There are 3 possibilities as shown below: | |||
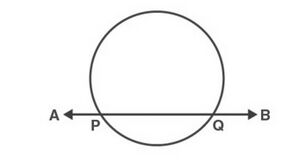
(1) Line <math>AB</math> intersects the circle at two points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> . Such a line is called ''secant'' of the circle. <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> are the points on the circle. <math>PQ</math> is a chord of the circle. | |||
[[File:Tangent intersecting.jpg|alt=Fig. 1|none|thumb|Fig. 1]] | |||
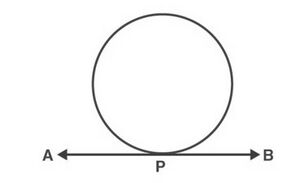
(2) Line <math>AB</math> touches the circle exactly at one point <math>P</math> . Such a line is called the ''tangent'' to the circle. | |||
[[File:Tangent touching.jpg|alt=Fig. 2|none|thumb|Fig. 2]] | |||
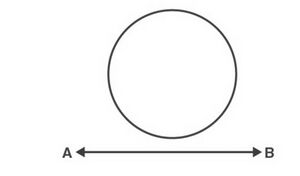
(3) Line <math>AB</math> does not touch the circle at any point and is referred to as a non-intersecting line. | |||
[[File:Tangent non-intersecting.jpg|alt=Fig. 3|none|thumb|Fig. 3]] | |||
== Tangent of a Circle Example == | |||
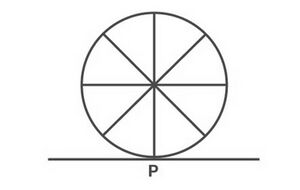
Imagine a bicycle moving on a road. If we look at its wheel, we observe that it touches the road at just one point. The road can be considered as a tangent to the wheel. | |||
[[File:Tangent wheel example.jpg|alt=Fig. 4|none|thumb|Fig. 4]]It is to be noted that there can one and only one tangent through any given point on the circle. | |||
Any other line through a point on the circle other than the tangent at that point would intersect the circle at two points. This can be easily seen from the following figure 5. | |||
[[File:Tangent two point intersection.jpg|alt=Fig. 5|none|thumb|Fig. 5]] | |||
<math>AB,CD,EF,GH,IJ</math> are a few lines passing through the point <math>P</math>, where <math>P</math> is a point on the circle. We observe that all the lines except <math>AB</math> pass through <math>P</math> and cut the circle at some other point. Hence only <math>AB</math> is a tangent and <math>CD,EF,GH,IJ</math> are secants to the circle. | |||
Every secant has a corresponding chord to the circle. Therefore, a tangent can be considered as a special case of secant when the endpoints of its corresponding chord coincide. | |||
[[Category:वृत्त]][[Category:गणित]][[Category:कक्षा-10]] | |||
Tangent of a circle | |||
Latest revision as of 09:16, 20 September 2024
A circle is a set of all points in a plane which are equally spaced from a fixed point. The fixed point is called the center of the circle and the distance between any point on the circle and its center is called the radius.
Definition
A tangent to a circle is a line which intersects the circle at only one point. The common point between the tangent and the circle are called the point of contact.
Given, a line to a circle could either be intersecting, non-intersecting or just touching the circle.
Consider any line and a circle. There are 3 possibilities as shown below:
(1) Line intersects the circle at two points and . Such a line is called secant of the circle. and are the points on the circle. is a chord of the circle.
(2) Line touches the circle exactly at one point . Such a line is called the tangent to the circle.
(3) Line does not touch the circle at any point and is referred to as a non-intersecting line.
Tangent of a Circle Example
Imagine a bicycle moving on a road. If we look at its wheel, we observe that it touches the road at just one point. The road can be considered as a tangent to the wheel.
It is to be noted that there can one and only one tangent through any given point on the circle.
Any other line through a point on the circle other than the tangent at that point would intersect the circle at two points. This can be easily seen from the following figure 5.
are a few lines passing through the point , where is a point on the circle. We observe that all the lines except pass through and cut the circle at some other point. Hence only is a tangent and are secants to the circle.
Every secant has a corresponding chord to the circle. Therefore, a tangent can be considered as a special case of secant when the endpoints of its corresponding chord coincide. Tangent of a circle