कार्टेशियन पद्धति: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(content added) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
बिंदु <math>A</math> का <math>x</math> निर्देशांक <math>Y</math>-अक्ष से बिंदु <math>A</math> की लंबवत दूरी है जो <math>2</math> इकाई है जो धनात्मक है। | बिंदु <math>A</math> का <math>x</math> निर्देशांक <math>Y</math>-अक्ष से बिंदु <math>A</math> की लंबवत दूरी है जो <math>2</math> इकाई है जो धनात्मक है। | ||
<math> | बिंदु <math>A</math> का <math>y</math> निर्देशांक <math>X</math>-अक्ष से बिंदु <math>A</math> की लंबवत दूरी है जो <math>4</math> इकाई है जो धनात्मक है। | ||
<math> | बिंदु <math>C</math> का <math>x</math> निर्देशांक <math>Y</math>-अक्ष से बिंदु <math>C</math> की लंबवत दूरी है जो <math>4</math> इकाई है जो ऋणात्मक है। | ||
<math> | बिंदु <math>C</math> का <math>y</math> निर्देशांक <math>X</math>-अक्ष से बिंदु <math>C</math> की लंबवत दूरी है जो <math>2</math> इकाई है जो ऋणात्मक है। | ||
<math>x</math> | <math>x</math> निर्देशांक को भुज भी कहा जाता है। | ||
<math>y</math> | <math>y</math> निर्देशांक को कोटि भी कहा जाता है। | ||
In stating the coordinates of a point in the coordinate plane, the <math>x</math> - coordinate comes first, and then the <math>y</math> - coordinate. We place the coordinates in brackets. Hence the coordinates of <math>A</math> are <math>(2,4)</math>, coordinates of <math>C</math> are <math>(-4,-2)</math>, | In stating the coordinates of a point in the coordinate plane, the <math>x</math> - coordinate comes first, and then the <math>y</math> - coordinate. We place the coordinates in brackets. Hence the coordinates of <math>A</math> are <math>(2,4)</math>, coordinates of <math>C</math> are <math>(-4,-2)</math>, | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 6 June 2024
कार्टेशियन निर्देशांक पद्धति गणित की एक शाखा है जो n-आयामी निर्देशांक तल में किसी बिंदु को विशिष्ट रूप से दर्शाने के तरीके के बारे में बताती है। कार्टेशियन पद्धति का सिद्धांत 17वीं शताब्दी में रेने डेसकार्टेस नामक एक फ्रांसीसी दार्शनिक और गणितज्ञ द्वारा प्रस्तावित किया गया था। इस कार्टेशियन निर्देशांक पद्धति ने यूक्लिडियन ज्यामिति और बीजगणित के बीच संबंध प्रदान किया, जिसने गणित के अध्ययन में क्रांति ला दी है। कार्टेशियन निर्देशांक पद्धति विश्लेषणात्मक ज्यामिति की नींव है और n-आयामी तल में रेखाओं, वक्रों और ज्यामितीय आकृतियों के प्रतिनिधित्व में मदद करती है।
कार्टेशियन पद्धति क्या है?
जिस पद्धति का उपयोग हम समतल में बिंदुओं को वर्गीकरण करने के लिए करते हैं उसे कार्टेशियन पद्धति के नाम से जाना जाता है। कार्टेशियन रूप संख्या रेखा से प्राप्त होता है। कार्टेशियन निर्देशांक पद्धति को समझने के लिए हमें संख्या रेखा के बारे में अच्छी तरह से जानना चाहिए। इस पद्धति में, हमारे पास निम्नलिखित परिभाषित मापदण्ड हैं जैसे:
दो लंबवत रेखाओं को -अक्ष और -अक्ष नाम दिया गया है।
इस तल को कार्टेशियन या निर्देशांक तल कहा जाता है और दो रेखाओं और को जब एक साथ रखा जाता है तो उन्हें पद्धति के निर्देशांक अक्ष कहा जाता है।
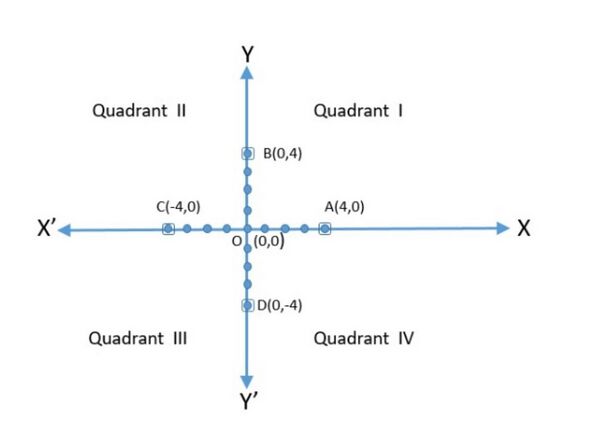
दो निर्देशांक अक्ष समतल को चार भागों में विभाजित करते हैं जिन्हें चतुर्भुज कहा जाता है जिन्हें , , और वामावर्त से कहा जाता है। इसलिए, समतल में अक्ष और ये चतुर्भुज होते हैं। हम समतल को कार्टेशियन तल या निर्देशांक तल या -तल कहते हैं। अक्षों को निर्देशांक अक्ष कहा जाता है।
अक्षों का प्रतिच्छेदन बिंदु कार्टेशियन प्रणाली का शून्य है। इस बिंदु को सामान्यतः द्वारा दर्शाया जाएगा। मूल के निर्देशांक को के रूप में दर्शाया जाता है।
समतल में किसी भी बिंदु की स्थिति निर्दिष्ट करने के लिए, हम की दूरी मापते हैं जिस पर हमें के साथ चलना है, और फिर की दूरी मापते हैं जो हमें के समानांतर चलना है, ताकि से तक पहुँच सकें। दूरियाँ ऋणात्मक हो सकती हैं।
उदाहरण के लिए, यदि आपको दाईं ओर बढ़ना है, तो धनात्मक होगा। इसी तरह, यदि आपको पर नीचे जाना है, तो ऋणात्मक होगा।
दो वास्तविक संख्याएँ और एक साथ आलेखित करने पर की स्थिति का विशिष्ट रूप से वर्णन होगा। हम इसे इस प्रकार लिख सकते हैं: [नीचे चित्र 1 से]। इस प्रकार, का स्थान दो वास्तविक संख्याओं द्वारा विशिष्ट रूप से वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है। के अलग-अलग पदों के लिए , वास्तविक संख्याओं का यह युग्म भिन्न होगा।
अब कार्टेशियन निर्देशांक के निम्नलिखित ग्राफिकल निरूपण को देखें और उपरोक्त विवरण को पुनः पढ़ें
आइए अक्षों से बिंदु और की दूरियाँ देखें। हम बिंदु और से -अक्ष और -अक्ष पर लंब खींचते हैं।
बिंदु का निर्देशांक -अक्ष से बिंदु की लंबवत दूरी है जो इकाई है जो धनात्मक है।
बिंदु का निर्देशांक -अक्ष से बिंदु की लंबवत दूरी है जो इकाई है जो धनात्मक है।
बिंदु का निर्देशांक -अक्ष से बिंदु की लंबवत दूरी है जो इकाई है जो ऋणात्मक है।
बिंदु का निर्देशांक -अक्ष से बिंदु की लंबवत दूरी है जो इकाई है जो ऋणात्मक है।
निर्देशांक को भुज भी कहा जाता है।
निर्देशांक को कोटि भी कहा जाता है।
In stating the coordinates of a point in the coordinate plane, the - coordinate comes first, and then the - coordinate. We place the coordinates in brackets. Hence the coordinates of are , coordinates of are ,
Since every point on the - axis has no distance (zero distance) from the - axis, therefore, the - coordinate of every point lying on the - axis is always zero. Thus, the coordinates of any point on the - axis are of the form (, ), where is the distance of the point from the - axis. Similarly, the coordinates of any point on the - axis are of the form (, ), where is the distance of the point from the - axis.
Graphical representation of zero distance Cartesian coordinates are shown below in Fig.2
What are the coordinates of the origin ? It has zero distance from both the axes so that its abscissa and ordinate are both zero. Therefore, the coordinates of the origin are .