विभाजन-सूत्र: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(added content) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
विभाजन-सूत्र का उपयोग उस बिंदु के निर्देशांक ज्ञात करने के लिए किया जाता है जो किसी रेखाखंड को (बाह्य या आंतरिक रूप से) किसी अनुपात में विभाजित करता है। | |||
== | == विभाजन-सूत्र की व्युत्पत्ति == | ||
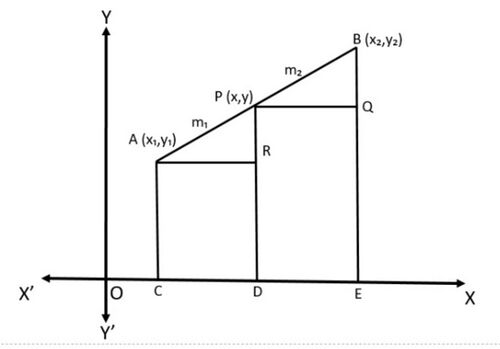
[[File:Section Formula.jpg|alt=Fig 1 - Section Formula|none|thumb|500x500px| | [[File:Section Formula.jpg|alt=Fig 1 - Section Formula|none|thumb|500x500px|चित्र -1 -विभाजन-सूत्र]] | ||
किन्हीं दो बिंदुओं <math>A(x_1,y_1)</math> और <math>B(x_2,y_2)</math> पर विचार करें और मान लीजिये <math>P(x,y)</math>, <math>AB</math> को आंतरिक रूप से अनुपात <math>m_1:m_2</math> में विभाजित करता है। | |||
i.e., <math>\frac{PA}{PB}=\frac{m_1}{m_2}</math> ( | i.e., <math>\frac{PA}{PB}=\frac{m_1}{m_2}</math> (चित्र 1 देखें) | ||
Draw <math>AC,PD,BE</math> perpendicular to the <math>x-</math>axis. Draw <math>AR,PQ</math> parallel to the <math>x-</math>axis. Then, by the <math>AA</math> similarity criterion, | Draw <math>AC,PD,BE</math> perpendicular to the <math>x-</math>axis. Draw <math>AR,PQ</math> parallel to the <math>x-</math>axis. Then, by the <math>AA</math> similarity criterion, | ||
<math>x-</math>अक्ष पर लंबवत <math>AC,PD,BE</math> खींचें। <math>x-</math>अक्ष के समानांतर <math>AR,PQ</math> खींचें। फिर, <math>AA</math> समानता मानदंड से, | |||
<math>\bigtriangleup PAR\sim \bigtriangleup BPQ</math> | <math>\bigtriangleup PAR\sim \bigtriangleup BPQ</math> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
<math>BQ=BE-QE=BE-PD=y_2-y</math> | <math>BQ=BE-QE=BE-PD=y_2-y</math> | ||
<math> (1)</math> प्रतिस्थापित करने पर हमें प्राप्त होता है | |||
<math>\frac{m_1}{m_2}=\frac{x-x_1}{x_2-x}=\frac{y-y_1}{y_2-y}</math> | <math>\frac{m_1}{m_2}=\frac{x-x_1}{x_2-x}=\frac{y-y_1}{y_2-y}</math> | ||
<math>\frac{m_1}{m_2}=\frac{x-x_1}{x_2-x}</math> लेने पर | |||
<math>m_1x_2-m_1x=m_2x-m_2x_1</math> | <math>m_1x_2-m_1x=m_2x-m_2x_1</math> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
<math>\frac{m_1}{m_2}=\frac{y-y_1}{y_2-y}</math> लेने पर | |||
<math>m_1y_2-m_1y=m_2y-m_2y_1</math> | <math>m_1y_2-m_1y=m_2y-m_2y_1</math> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
<math>y=\frac{m_1y_2+m_2y_1}{m_1+m_2}</math> | <math>y=\frac{m_1y_2+m_2y_1}{m_1+m_2}</math> | ||
इसलिए, बिंदु <math>P(x,y)</math> के निर्देशांक जो बिंदु <math>A(x_1,y_1)</math> और <math>B(x_2,y_2)</math> को मिलाने वाले रेखाखंड को आंतरिक रूप से किस अनुपात में विभाजित करते हैं | |||
<math>m_1:m_2</math> are <math>\left (\frac{m_1x_2+m_2x_1}{m_1+m_2},\frac{m_1y_2+m_2y_1}{m_1+m_2} \right )</math> विभाजन-सूत्र है। | |||
=== | === उदाहरण === | ||
उस बिंदु के निर्देशांक ज्ञात करें जो बिंदुओं <math>(4,-3)</math> और <math>(8,5) | |||
</math> को मिलाने वाले रेखाखंड को <math>3:1</math> के अनुपात में आंतरिक रूप से विभाजित करता है। | |||
''' | '''हल''' : <math>P(x,y)</math> को वांछित बिंदु मान लें। | ||
<math>x_1=4,y_1=-3</math> | <math>x_1=4,y_1=-3</math> | ||
<math>x_2=8,y_2=5</math> | <math>x_2=8,y_2=5</math> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 67: | ||
विभाजन-सूत्र का उपयोग करते हुए, हम प्राप्त करते | |||
<math>x=\frac{m_1x_2+m_2x_1}{m_1+m_2}</math> | <math>x=\frac{m_1x_2+m_2x_1}{m_1+m_2}</math> | ||
| Line 75: | Line 79: | ||
अतः <math>(7,3)</math> ही अभीष्ट बिंदु है। | |||
[[Category:निर्देशांक ज्यामिति]][[Category:गणित]][[Category:कक्षा-10]] | [[Category:निर्देशांक ज्यामिति]][[Category:गणित]][[Category:कक्षा-10]] | ||
Revision as of 10:16, 19 June 2024
विभाजन-सूत्र का उपयोग उस बिंदु के निर्देशांक ज्ञात करने के लिए किया जाता है जो किसी रेखाखंड को (बाह्य या आंतरिक रूप से) किसी अनुपात में विभाजित करता है।
विभाजन-सूत्र की व्युत्पत्ति
किन्हीं दो बिंदुओं और पर विचार करें और मान लीजिये , को आंतरिक रूप से अनुपात में विभाजित करता है।
i.e., (चित्र 1 देखें)
Draw perpendicular to the axis. Draw parallel to the axis. Then, by the similarity criterion,
अक्ष पर लंबवत खींचें। अक्ष के समानांतर खींचें। फिर, समानता मानदंड से,
प्रतिस्थापित करने पर हमें प्राप्त होता है
लेने पर
लेने पर
इसलिए, बिंदु के निर्देशांक जो बिंदु और को मिलाने वाले रेखाखंड को आंतरिक रूप से किस अनुपात में विभाजित करते हैं
are विभाजन-सूत्र है।
उदाहरण
उस बिंदु के निर्देशांक ज्ञात करें जो बिंदुओं और को मिलाने वाले रेखाखंड को के अनुपात में आंतरिक रूप से विभाजित करता है।
हल : को वांछित बिंदु मान लें।
विभाजन-सूत्र का उपयोग करते हुए, हम प्राप्त करते
अतः ही अभीष्ट बिंदु है।