त्रिभुज के गुण: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(added content) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
प्रमेय 1: समद्विबाहु त्रिभुज की समान भुजाओं के सम्मुख कोण समान होते हैं | |||
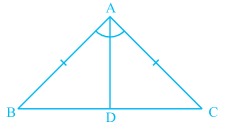
[[File:Isosceles Triangle -1.jpg|alt=Fig 1 - Isosceles triangle|none|thumb| | [[File:Isosceles Triangle -1.jpg|alt=Fig 1 - Isosceles triangle|none|thumb|चित्र 1- समद्विबाहु त्रिभुज]] | ||
प्रमाण: चित्र 1 में दिखाए गए समद्विबाहु त्रिभुज <math>BCA</math> पर विचार करें, जहाँ <math>AB=AC</math> है। | |||
हमें यह सिद्ध करना होगा कि भुजाओं <math>AB</math>और <math>AC</math> के सम्मुख कोण समान अर्थात् <math>\angle ABC = \angle ACB</math> हैं। | |||
हम पहले <math>\angle BAC</math>का एक समद्विभाजक बनाते हैं और इसे <math>AD</math> नाम देते हैं। | |||
अब <math>\triangle BAD</math> और <math>\triangle CAD</math> में हमारे पास है, | |||
<math>AB=AC</math> ( | <math>AB=AC</math> (दिया हुआ) | ||
<math>\angle BAD =\angle CAD </math> ( | <math>\angle BAD =\angle CAD </math> (संरचना से) | ||
<math>AD=AD</math> ( | <math>AD=AD</math> (दोनों में समान) | ||
अत:, <math>\triangle BAD \cong \triangle CAD</math> (SAS सर्वांगसमता मानदंड द्वारा) | |||
इसलिए, <math>\angle ABC =\angle ACB </math> (CPCT द्वारा) | |||
अतः सिद्ध हुआ। | |||
Revision as of 10:46, 18 September 2024
प्रमेय 1: समद्विबाहु त्रिभुज की समान भुजाओं के सम्मुख कोण समान होते हैं
प्रमाण: चित्र 1 में दिखाए गए समद्विबाहु त्रिभुज पर विचार करें, जहाँ है।
हमें यह सिद्ध करना होगा कि भुजाओं और के सम्मुख कोण समान अर्थात् हैं।
हम पहले का एक समद्विभाजक बनाते हैं और इसे नाम देते हैं।
अब और में हमारे पास है,
(दिया हुआ)
(संरचना से)
(दोनों में समान)
अत:, (SAS सर्वांगसमता मानदंड द्वारा)
इसलिए, (CPCT द्वारा)
अतः सिद्ध हुआ।
Theorem 2: The sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal.
Proof: In a triangle shown in fig 1, base angles are equal and we need to prove that or is an isosceles triangle.
Construct a bisector which meets the side at right angles.
Now in and we have,
(By construction)
(Common side)
(By construction)
Thus, (By ASA congruence criterion)
So, (By CPCT)
Or is isosceles.