त्रिज्यखंड और वृत्तखंड के क्षेत्रेफल: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(content modified) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | == त्रिज्यखंड == | ||
[[File:Sector.jpg|alt=Fig. 1 - Sector|thumb|150x150px| | [[File:Sector.jpg|alt=Fig. 1 - Sector|thumb|150x150px|चित्र 1 -त्रिज्यखंड ]] | ||
The circular region between two radii of a circle and the arc between them is called a sector of the circle. The sector always starts from the center of the circle. The semi-circle is also called the sector of the circle. | The circular region between two radii of a circle and the arc between them is called a sector of the circle. The sector always starts from the center of the circle. The semi-circle is also called the sector of the circle. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Angle of major sector is <math>360^\circ-\angle AOB</math>. | Angle of major sector is <math>360^\circ-\angle AOB</math>. | ||
== | == वृत्तखंड == | ||
[[File:Segment.jpg|alt=Fig. 2 - Segment|thumb|150x150px| | [[File:Segment.jpg|alt=Fig. 2 - Segment|thumb|150x150px|चित्र 2 -वृत्तखंड]] | ||
The part of the circular region enclosed between a chord and the corresponding arc is called a segment of the circle. | The part of the circular region enclosed between a chord and the corresponding arc is called a segment of the circle. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== | == त्रिज्यखंड का क्षेत्रफल == | ||
[[File:Sector-1.jpg|alt=Fig 3 - Sector|thumb|150x150px| | [[File:Sector-1.jpg|alt=Fig 3 - Sector|thumb|150x150px|चित्र 3 -त्रिज्यखंड ]] | ||
Let us find the the area of a sector. | Let us find the the area of a sector. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Length and area of the arc <math>APB</math>''' '''corresponding to the sector <math>OAPB</math>''' | '''Length and area of the arc <math>APB</math>''' '''corresponding to the sector <math>OAPB</math>''' | ||
[[File:Sector-length.jpg|alt=Fig 4 - Sector|thumb|151x151px| | [[File:Sector-length.jpg|alt=Fig 4 - Sector|thumb|151x151px|चित्र 4 -त्रिज्यखंड ]] | ||
In the Fig 4. | In the Fig 4. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
Area of major segment '''<math>AQB</math>''' = <math>\Pi r^2</math> – Area of the minor segment '''<math>APB</math>''' | Area of major segment '''<math>AQB</math>''' = <math>\Pi r^2</math> – Area of the minor segment '''<math>APB</math>''' | ||
== | == उदाहरण == | ||
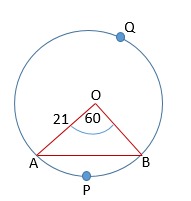
[[File:Sector-segment problem.jpg|alt=Example - 1|thumb| | [[File:Sector-segment problem.jpg|alt=Example - 1|thumb|उदाहरण- 1]] | ||
In a circle of radius <math>21</math> cm, an arc subtends an angle of <math>60^\circ</math>at the centre. | In a circle of radius <math>21</math> cm, an arc subtends an angle of <math>60^\circ</math>at the centre. | ||
Revision as of 07:09, 27 August 2024
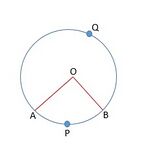
त्रिज्यखंड
The circular region between two radii of a circle and the arc between them is called a sector of the circle. The sector always starts from the center of the circle. The semi-circle is also called the sector of the circle.
There are two types of sectors namely minor sector and major sector.
In Fig. 1 is a sector of the circle with centre . is called the angle of sector. is called the minor sector and is called the major sector.
Angle of major sector is .
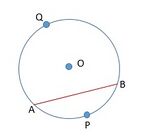
वृत्तखंड
The part of the circular region enclosed between a chord and the corresponding arc is called a segment of the circle.
In Fig. 2 is a chord of the circle with centre . is a segment of the circle.
There are two types of segment namely minor segment and major segment.
is called the minor segment and is called the major segment.
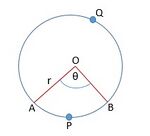
त्रिज्यखंड का क्षेत्रफल
Let us find the the area of a sector.
In the Fig 3 . Let be a sector of a circle with centre and radius and be .
We know the area of a circle is .
When the degree of measure of the angle at the centre is , area of the sector =
Hence when the degree of measure of the angle at the centre is , area of the sector =
| Area of the sector of angle where is the radius of the circle and the angle of the sector in degrees. |
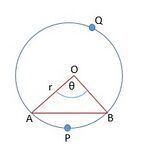
Length and area of the arc corresponding to the sector
In the Fig 4.
When the degree of measure of the angle at the centre is , length of the arc=
Hence when the degree of measure of the angle at the centre is , length of the arc=
| Length of the arc = |
Area of the segment = Area of the sector - Area of the
From Fig 3 and Fig 4
Area of the major sector = – Area of the minor sector
Area of major segment = – Area of the minor segment
उदाहरण
In a circle of radius cm, an arc subtends an angle of at the centre.
Find:
(i) the length of the arc (ii) area of the sector formed by the arc (iii) area of the segment formed by the corresponding chord
Here
(i) length of the arc =
= = = cm
(ii) area of the sector =
= = = cm2
(iii) area of the segment formed by the corresponding chord = area of the sector - area of the triangle
=
=
= cm2