Theorem 1: Angles opposite to equal sides of an isosceles triangle are equal
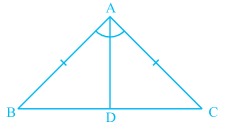
Fig 1 - Isosceles triangle
Proof: Consider an isosceles triangle  shown in fig 1 where
shown in fig 1 where  .
.
We need to prove that the angles opposite to the sides  and
and  are equal, that is,
are equal, that is, 
We first draw a bisector of  and name it as
and name it as  .
.
Now in  and
and  we have,
we have,
 (Given)
(Given)
 (By construction)
(By construction)
 (Common to both)
(Common to both)
Thus,  (By SAS congruence criterion)
(By SAS congruence criterion)
So,  (By CPCT)
(By CPCT)
Hence proved.
Theorem 2: The sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal.
Proof: In a triangle  shown in fig 1, base angles are equal and we need to prove that
shown in fig 1, base angles are equal and we need to prove that  or
or  is an isosceles triangle.
is an isosceles triangle.
Construct a bisector  which meets the side
which meets the side  at right angles.
at right angles.
Now in  and
and  we have,
we have,
 (By construction)
(By construction)
 (Common side)
(Common side)
 (By construction)
(By construction)
Thus,  (By ASA congruence criterion)
(By ASA congruence criterion)
So,  (By CPCT)
(By CPCT)
Or  is isosceles.
is isosceles.
