रैखिक समीकरण
What is a Linear Equation?
An equation that has the highest degree of is known as a linear equation. This means that no variable in a linear equation has a variable whose exponent is more than . The graph of a linear equation always forms a straight line.
Linear Equation Definition: A linear equation is an algebraic equation where each term has an exponent of and when this equation is graphed, it always results in a straight line. This is the reason why it is named as a 'linear' equation.
There are linear equations in one variable and linear equations in two variables. Let us learn how to identify linear equations and non-linear equations with the help of the following examples.
| Equations | Linear or Non-Linear |
|---|---|
| Linear | |
| Non-Linear, the power of the variable is 2 | |
| Non-Linear, the power of the variable is 1/2 | |
| Linear | |
| Non-Linear, the power of the variable is 2 |
Linear Equations in Standard Form
The standard form or the general form of linear equations in one variable is written as, where and are real numbers, and is the single variable.
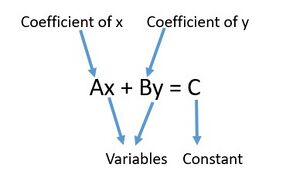
The standard form of linear equations in two variables is expressed as, where , and are any real numbers, and and are the variables.
Linear Equations in One Variable
A linear equation in one variable is an equation in which there is only one variable present. It is of the form , where and are any two real numbers and is an unknown variable that has only one solution. It is the easiest way to represent a mathematical statement. This equation has a degree that is always equal to . A linear equation in one variable can be solved very easily. The variables are separated and brought to one side of the equation and the constants are combined and brought to the other side of the equation, to get the value of the unknown variable
Example: Solve the linear equation in one variable: .
In order to solve the given equation, we bring the numbers on the right-hand side of the equation and we keep the variable on the left-hand side. This means, . Then, as we solve for , we get, . Finally, the value of .
Linear Equations in Two Variables
A linear equation in two variables is of the form , in which , , are real numbers and and are the two variables, each with a degree of . If we consider two such linear equations, they are called simultaneous linear equations. For example, is a linear equation in two variables. There are various ways of solving linear equations in two variables like the graphical method, the substitution method, the cross multiplication method, the elimination method, and the determinant method.
Problem 1:
Write each of the following equation in the form and indicate the values of , and in each case:
Solution:
, Here
Problem 2:
Write each of the following as an equation in two variables.
(i) -----
(i) ----- रैखिक समीकरण, एक बीजीय समीकरण है जिसमें चर की उच्चतम घात हमेशा 1 होती है। इसे एक-घातीय समीकरण के रूप में भी जाना जाता है। जब इस समीकरण को रेखांकन किया जाता है, तो इसका परिणाम प्रायः एक सीधी रेखा में होता है। इसलिए इसे 'रैखिक' समीकरण का नाम दिया गया है।
एक चर में रैखिक समीकरण का मानक रूप के रूप का होता है। यहाँ, एक चर है, एक गुणांक है, और स्थिरांक है।
दो चर वाले रैखिक समीकरण का मानक रूप इस प्रकार का होता है
यहां, और चर हैं, और गुणांक हैं, और एक स्थिरांक है।
एक चर में रैखिक समीकरण का उदाहरण
दो चर वाले रैखिक समीकरण का उदाहरण
समस्या 1 :
निम्नलिखित समीकरणों में से प्रत्येक को ax + by + c = 0 के रूप में लिखें और प्रत्येक स्थिति में a, b और c के मान इंगित करें:
हल:
, यहाँ
समस्या 2 :
निम्नलिखित में से प्रत्येक को दो चरों वाले समीकरण के रूप में लिखिए।
(i) -----
(i) -----