अभिगृहीत
अभिगृहीत एक सार्वभौमिक सत्य है जिसका कोई प्रमाण नहीं है, और जो ज्यामिति से विशेष रूप से जुड़ा हुआ नहीं है।अभिगृहीत का एक उदाहरण यह कथन है कि "समान के आधे भाग समान होते हैं"।
अभिगृहीत 1: जो वस्तुएँ एक ही वस्तु के समान हैं वे एक दूसरे के समान हैं।
मान लीजिए कि एक आयत का क्षेत्रफल एक त्रिभुज के क्षेत्रफल के बराबर है और उस त्रिभुज का क्षेत्रफल एक वर्ग के क्षेत्रफल के बराबर है। पहले अभिगृहीत को लागू करने के बाद, हम कह सकते हैं कि एक आयत और वर्ग का क्षेत्रफल बराबर है। उदाहरण के लिए, यदि और है, तो हम कह सकते हैं
अभिगृहीत 2: यदि समान को समान में जोड़ा जाए, तो पूर्ण समान होते हैं।
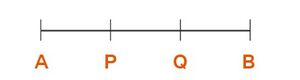
आइए चित्र-1 में रेखाखंड को देखें, जहाँ है। जब दोनों पक्षों में जोड़ दिया जाता है, तो अभिगृहीत 2 के अनुसार, i.e .
Axiom 3: If equals are subtracted from equals, the remainders are equal.
Axiom 4: Things that coincide with one another are equal to one another.
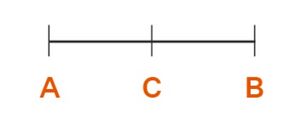
Consider line segment with in the center. coincides with the line segment . Thus by axiom 4, we can say that .
Axiom 5: The whole is greater than the part.
Using the same figure as above, is a part of . Thus according to axiom 5, we can say that .
Axiom 6 and Axiom 7: Things that are double of the same things are equal to one another. Things that are halves of the same things are equal to one another.
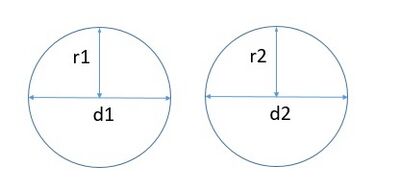
Axiom 6 and 7 are interrelated. Consider two identical circles with radii and with diameters as and respectively. Since the circles are identical, using both axioms 6 and 7, we can say that
= and =