त्रिज्यखंड
किसी वृत्त की दो त्रिज्याओं के बीच का वृत्ताकार क्षेत्र और उनके बीच का चाप वृत्त का त्रिज्यखंड कहलाता है। सेक्टर सदैव वृत्त के केंद्र से प्रारंभ होता है। अर्धवृत्त को वृत्त का त्रिज्यखंड भी कहा जाता है।
त्रिज्यखंड दो प्रकार के होते हैं, लघु त्रिज्यखंड और दीर्घ त्रिज्यखंड।
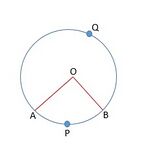
चित्र 1 में  , केंद्र
, केंद्र  सहित वृत्त का एक त्रिज्यखंड है।
सहित वृत्त का एक त्रिज्यखंड है।  को त्रिज्यखंड का कोण कहा जाता है।
को त्रिज्यखंड का कोण कहा जाता है।  को लघु त्रिज्यखंड कहा जाता है और
को लघु त्रिज्यखंड कहा जाता है और  को दीर्घ त्रिज्यखंड कहा जाता है।
को दीर्घ त्रिज्यखंड कहा जाता है।
दीर्घ त्रिज्यखंड का कोण  है।
है।
वृत्तखंड
किसी जीवा और संगत चाप के बीच घिरे वृत्ताकार क्षेत्र के भाग को वृत्त का खंड कहा जाता है।
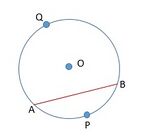
चित्र 2 में  केंद्र
केंद्र  वाले वृत्त की एक जीवा है।
वाले वृत्त की एक जीवा है।
 वृत्त का एक खंड है।
वृत्त का एक खंड है।
खंड दो प्रकार के होते हैं, लघु खंड और दीर्घ खंड।
 को लघु खंड और कहा जाता है
को लघु खंड और कहा जाता है
 को दीर्घ खंड कहा जाता है।
को दीर्घ खंड कहा जाता है।
त्रिज्यखंड का क्षेत्रफल
आइए एक त्रिज्यखंड का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात करें।
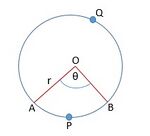
चित्र 3 में. चलो मान लें कि  एक वृत्त का त्रिज्यखंड है जिसका केंद्र
एक वृत्त का त्रिज्यखंड है जिसका केंद्र  , और त्रिज्या
, और त्रिज्या  है तथा
है तथा  , 𝜃 है।
, 𝜃 है।
हम जानते हैं कि एक वृत्त का क्षेत्रफल  है।
है।
जब केंद्र पर कोण के माप का घात  है, तो त्रिज्यखंड का क्षेत्रफल =
है, तो त्रिज्यखंड का क्षेत्रफल =  है, इसलिए जब केंद्र पर कोण के माप का घात
है, इसलिए जब केंद्र पर कोण के माप का घात  है,
है,
तो त्रिज्यखंड का क्षेत्रफल =
Area of the sector of angle  where is where is  the radius of the circle and the radius of the circle and  the angle of the sector in degrees. the angle of the sector in degrees.
|
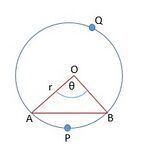
चाप की लम्बाई एवं क्षेत्रफल  , त्रिज्यखंड
, त्रिज्यखंड  के अनुरूप
के अनुरूप
चित्र 4 में।
When the degree of measure of the angle at the centre is  , length of the arc=
, length of the arc= 
Hence when the degree of measure of the angle at the centre is  , length of the arc=
, length of the arc= 
Length of the arc = 
|
Area of the segment  = Area of the sector
= Area of the sector  - Area of the
- Area of the 
From Fig 3 and Fig 4
Area of the major sector  =
=  – Area of the minor sector
– Area of the minor sector 
Area of major segment  =
=  – Area of the minor segment
– Area of the minor segment 
उदाहरण
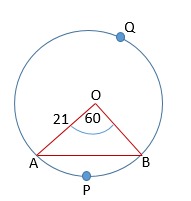
In a circle of radius  cm, an arc subtends an angle of
cm, an arc subtends an angle of  at the centre.
at the centre.
Find:
(i) the length of the arc (ii) area of the sector formed by the arc (iii) area of the segment formed by the corresponding chord
Here 

(i) length of the arc  =
= 
= =
=  =
=  cm
cm
(ii) area of the sector  =
= 
=  =
=  =
=  cm2
cm2
(iii) area of the segment  formed by the corresponding chord = area of the sector
formed by the corresponding chord = area of the sector  - area of the triangle
- area of the triangle 
= 
= 
= ![{\displaystyle \left[231-{\frac {441{\sqrt {3}}}{4}}\right]}](/index.php?title=Special:MathShowImage&hash=61c4d2889ee89a449e3bb4893248bc40&mode=mathml) cm2
cm2