|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| In this section, we will find the values of the trigonometric ratios for angles of <math>0^\circ ,30^\circ , 45^\circ, 60^\circ , 90^\circ
| | इस अनुभाग में, हम <math>0^\circ ,30^\circ , 45^\circ, 60^\circ , 90^\circ |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| </math>. | | </math>के कोणों के लिए त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपातों के मान ज्ञात करेंगे। |
|
| |
|
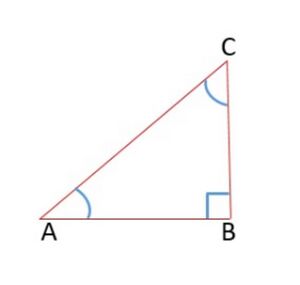
| == Trigonometric Ratios of 45° == | | == 45° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात == |
| [[File:Right angle triangle.jpg|alt=Fig.1 Triangle|thumb|Fig.1 Triangle]] | | [[File:Right angle triangle.jpg|alt=Fig.1 Triangle|thumb|चित्र -1 त्रिभुज]] |
| In <math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math> right angled at <math>B</math> , If <math>\angle A =45^\circ</math>, <math>\angle C =45^\circ</math> | | In <math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math> right angled at <math>B</math> , If <math>\angle A =45^\circ</math>, <math>\angle C =45^\circ</math> |
|
| |
|
| Line 26: |
Line 26: |
| <math>cosec \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{sin \ 45^\circ}=\sqrt{2}</math> , <math>sec \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{cos \ 45^\circ}=\sqrt{2}</math> , <math>cot \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{tan \ 45^\circ}=1</math> | | <math>cosec \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{sin \ 45^\circ}=\sqrt{2}</math> , <math>sec \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{cos \ 45^\circ}=\sqrt{2}</math> , <math>cot \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{tan \ 45^\circ}=1</math> |
|
| |
|
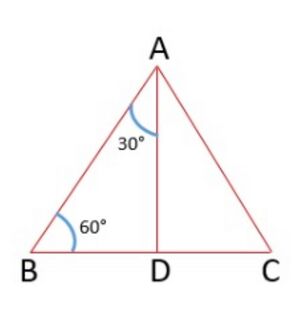
| == Trigonometric Ratios of 30° and 60° == | | == 30° और 60° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात == |
| [[File:Triangle -1.jpg|alt=Fig. 2 - Triangle|thumb|Fig. 2 Triangle]] | | [[File:Triangle -1.jpg|alt=Fig. 2 - Triangle|thumb|चित्र -2 त्रिभुज]] |
| Consider an equilateral <math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math>. Each angle in an equilateral triangle is <math>60^\circ</math>, therefore,<math>\angle A = \angle B =\angle C =60^\circ</math> . | | Consider an equilateral <math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math>. Each angle in an equilateral triangle is <math>60^\circ</math>, therefore,<math>\angle A = \angle B =\angle C =60^\circ</math> . |
|
| |
|
| Line 57: |
Line 57: |
|
| |
|
| {| class="wikitable" | | {| class="wikitable" |
| |+Trigonometric ratios of 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90° | | |+0°, 30°, 45°, 60° और 90° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात |
| !<math>\angle A</math> | | !<math>\angle A</math> |
| !<math>0^\circ</math> | | !<math>0^\circ</math> |
| Line 84: |
Line 84: |
| |<math>1</math> | | |<math>1</math> |
| |<math>\sqrt{3} </math> | | |<math>\sqrt{3} </math> |
| |Not Defined | | |अपरिभाषित |
| |- | | |- |
| |<math>cosec \ A</math> | | |<math>cosec \ A</math> |
| |Not Defined | | |अपरिभाषित |
| |<math>2</math> | | |<math>2</math> |
| |<math>\sqrt{2} </math> | | |<math>\sqrt{2} </math> |
| Line 98: |
Line 98: |
| |<math>\sqrt{2} </math> | | |<math>\sqrt{2} </math> |
| |<math>2</math> | | |<math>2</math> |
| |Not Defined | | |अपरिभाषित |
| |- | | |- |
| |<math>cot \ A</math> | | |<math>cot \ A</math> |
| |Not Defined | | |अपरिभाषित |
| |<math>\sqrt{3} </math> | | |<math>\sqrt{3} </math> |
| |<math>1</math> | | |<math>1</math> |
इस अनुभाग में, हम  के कोणों के लिए त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपातों के मान ज्ञात करेंगे।
के कोणों के लिए त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपातों के मान ज्ञात करेंगे।
45° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात
In  right angled at
right angled at  , If
, If  ,
, 

Using Pythagoras Theorem






 ,
,  ,
, 
30° और 60° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात
Consider an equilateral  . Each angle in an equilateral triangle is
. Each angle in an equilateral triangle is  , therefore,
, therefore, .
.
Draw a perpendicular  from
from  to the side
to the side  (see Fig. 2).
(see Fig. 2).
Now 
Therefore,  and
and  (Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles)
(Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles)
 is a right angled triangle , right angled at
is a right angled triangle , right angled at  with
with  and
and 
Let  , Hence
, Hence 



 ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
, 
Similarly
 ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
, 
0°, 30°, 45°, 60° और 90° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
अपरिभाषित
|

|
अपरिभाषित
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
अपरिभाषित
|

|
अपरिभाषित
|

|

|

|

|