कुछ विशिष्ट कोणों के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात: Difference between revisions
From Vidyalayawiki
No edit summary |
Ramamurthy (talk | contribs) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
इस अनुभाग में, हम <math>0^\circ ,30^\circ , 45^\circ, 60^\circ , 90^\circ | |||
[[Category:त्रिकोणमिति]] | |||
</math>के कोणों के लिए त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपातों के मान ज्ञात करेंगे। | |||
== 45° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात == | |||
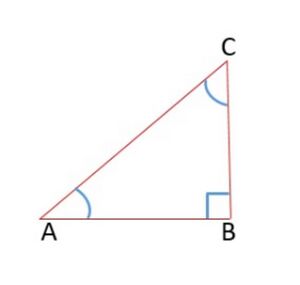
[[File:Right angle triangle.jpg|alt=Fig.1 Triangle|thumb|चित्र -1 त्रिभुज]] | |||
<math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math> में <math>B</math> समकोण है, यदि <math>\angle A =45^\circ</math>, <math>\angle C =45^\circ</math> | |||
<math>BC=AB=a</math> | |||
पाइथागोरस प्रमेय का उपयोग करते हुए | |||
<math>AB^2+BC^2=AC^2</math> | |||
<math>a^2+a^2=2a^2</math> | |||
<math>AC= a\sqrt{2} </math> | |||
<math>sin \ 45^\circ = \frac{side \ opposite \ to \ angle \ 45^\circ}{hypotenuse}= \frac{BC} {AC} =\frac{a} {a\sqrt{2}}=\frac{1} {\sqrt{2}}</math> | |||
<math>cos \ 45^\circ = \frac{side \ adjacent \ to \ angle \ 45^\circ}{hypotenuse}= \frac{AB} {AC} =\frac{a} {a\sqrt{2}}=\frac{1} {\sqrt{2}}</math> | |||
<math>tan \ 45^\circ = \frac{side \ opposite \ to \ angle \ 45^\circ}{side \ adjacent \ to \ angle \ 45^\circ}= \frac{BC}{AB} =\frac{a}{a}=1</math> | |||
<math>cosec \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{sin \ 45^\circ}=\sqrt{2}</math> , <math>sec \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{cos \ 45^\circ}=\sqrt{2}</math> , <math>cot \ 45^\circ = \frac{1}{tan \ 45^\circ}=1</math> | |||
== 30° और 60° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात == | |||
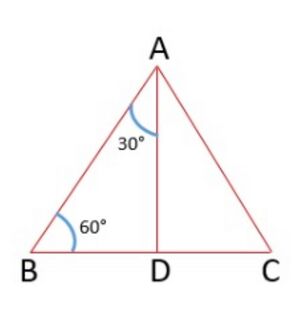
[[File:Triangle -1.jpg|alt=Fig. 2 - Triangle|thumb|चित्र -2 त्रिभुज]] | |||
समबाहु <math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math> पर विचार करें। समबाहु त्रिभुज में प्रत्येक कोण <math>60^\circ</math> होता है, इसलिए, <math>\angle A = \angle B =\angle C =60^\circ</math> . | |||
<math>A</math> से भुजा <math>BC</math> तक एक लंब <math>AD</math> खींचिए (चित्र-2 देखें)। | |||
अब <math>\bigtriangleup ABD=\bigtriangleup ACD</math> | |||
अतः, <math>BD=DC</math> और <math>\angle BAD = \angle CAD</math> (सर्वांगसम त्रिभुजों के संगत भाग) | |||
<math>\bigtriangleup ABD</math> एक समकोण त्रिभुज है, जो <math>\angle BAD = 30^\circ</math> और <math>\angle ABD = 60^\circ</math> के साथ <math>D</math> पर समकोण है। | |||
मान लीजिए <math>AB=2a</math> , अत: <math>BC=AC=AB=2a</math> | |||
<math>BD=\frac{1}{2}BC=\frac{1}{2} \times 2a=a</math> | |||
<math>AD^2=AB^2-BD^2=(2a)^2-a^2=3a^2</math> | |||
<math>AD=a\sqrt{3}</math> | |||
<math>sin \ 30^\circ = \ \frac{BD} {AB} =\frac{a} {2a}=\frac{1} {2}</math> , <math>cos \ 30^\circ = \ \frac{AD} {AB} =\frac{a\sqrt{3}} {2a}=\frac{\sqrt{3}} {2}</math> , <math>tan \ 30^\circ = \ \frac{BD} {AD} =\frac{a} {a\sqrt{3}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} </math> | |||
<math>cosec \ 30^\circ = \frac{1}{sin \ 30^\circ}=2</math> , <math>sec \ 30^\circ = \frac{1}{cos \ 30^\circ}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}</math> , <math>cot \ 30^\circ = \frac{1}{tan \ 30^\circ}=\sqrt{3}</math> | |||
इसी प्रकार | |||
<math>sin \ 60^\circ = \ \frac{AD} {AB} =\frac{a\sqrt{3}} {2a}=\frac{\sqrt{3}} {2}</math> , <math>cos \ 60^\circ = \ \frac{BD} {AB} =\frac{a} {2a}=\frac{1} {2}</math> , <math>tan \ 60^\circ = \ \frac{AD} {BD} =\frac{a\sqrt{3}} {a}=\sqrt{3} </math> | |||
<math>cosec \ 60^\circ = \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}</math> , <math>sec \ 60^\circ = \frac{1}{cos \ 60^\circ}=2</math> , <math>cot \ 60^\circ = \frac{1}{tan \ 60^\circ}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}</math> | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+0°, 30°, 45°, 60° और 90° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात | |||
!<math>\angle A</math> | |||
!<math>0^\circ</math> | |||
!<math>30^\circ</math> | |||
!<math>45^\circ</math> | |||
!<math>60^\circ</math> | |||
!<math>90^\circ</math> | |||
|- | |||
|<math>sin \ A</math> | |||
|<math>0</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{1} {2}</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{\sqrt{3}} {2}</math> | |||
|<math>1</math> | |||
|- | |||
|<math>cos \ A</math> | |||
|<math>1</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{\sqrt{3}} {2}</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{1} {2}</math> | |||
|<math>0</math> | |||
|- | |||
|<math>tan \ A</math> | |||
|<math>0</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}</math> | |||
|<math>1</math> | |||
|<math>\sqrt{3} </math> | |||
|अपरिभाषित | |||
|- | |||
|<math>cosec \ A</math> | |||
|अपरिभाषित | |||
|<math>2</math> | |||
|<math>\sqrt{2} </math> | |||
|<math>\frac {2}{\sqrt{3}}</math> | |||
|<math>1</math> | |||
|- | |||
|<math>sec \ A</math> | |||
|<math>1</math> | |||
|<math>\frac {2}{\sqrt{3}}</math> | |||
|<math>\sqrt{2} </math> | |||
|<math>2</math> | |||
|अपरिभाषित | |||
|- | |||
|<math>cot \ A</math> | |||
|अपरिभाषित | |||
|<math>\sqrt{3} </math> | |||
|<math>1</math> | |||
|<math>\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}</math> | |||
|<math>0</math> | |||
|} | |||
[[Category:त्रिकोणमिति का परिचय]] | |||
[[Category:गणित]] | |||
[[Category:कक्षा-10]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:13, 26 September 2024
इस अनुभाग में, हम के कोणों के लिए त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपातों के मान ज्ञात करेंगे।
45° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात
में समकोण है, यदि ,
पाइथागोरस प्रमेय का उपयोग करते हुए
, ,
30° और 60° के त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपात
समबाहु पर विचार करें। समबाहु त्रिभुज में प्रत्येक कोण होता है, इसलिए, .
से भुजा तक एक लंब खींचिए (चित्र-2 देखें)।
अब
अतः, और (सर्वांगसम त्रिभुजों के संगत भाग)
एक समकोण त्रिभुज है, जो और के साथ पर समकोण है।
मान लीजिए , अत:
, ,
, ,
इसी प्रकार
, ,
, ,
| अपरिभाषित | |||||
| अपरिभाषित | |||||
| अपरिभाषित | |||||
| अपरिभाषित |