जीवा द्वारा एक बिंदु पर अंतरित कोण: Difference between revisions
From Vidyalayawiki
No edit summary |
(New Mathematics Class 9 Hindi Page Created) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | '''प्रमेय 1''': एक वृत्त की समान जीवाएँ केंद्र पर समान कोण अंतरित करती हैं। | ||
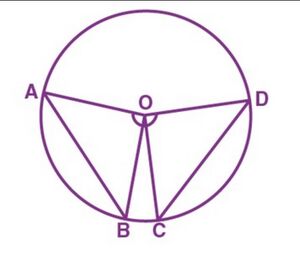
'''Proof''' :Consider a circle and draw two equal chords <math>AB</math> and <math>CD</math> of a circle with center <math>O</math> as shown in the figure 1. | '''Proof''' :Consider a circle and draw two equal chords <math>AB</math> and <math>CD</math> of a circle with center <math>O</math> as shown in the figure 1. | ||
[[File:Angle-subtend-chord-point.jpg|alt=Angle-subtend-chord-point|thumb| | [[File:Angle-subtend-chord-point.jpg|alt=Angle-subtend-chord-point|thumb|चित्र -1]] | ||
We want to prove that : <math>\angle AOB = \angle COD </math> | We want to prove that : <math>\angle AOB = \angle COD </math> | ||
Revision as of 15:02, 23 August 2024
प्रमेय 1: एक वृत्त की समान जीवाएँ केंद्र पर समान कोण अंतरित करती हैं।
Proof :Consider a circle and draw two equal chords and of a circle with center as shown in the figure 1.
We want to prove that :
From the triangles, and , we get
(Radii of a circle)
(Radii of a circle)
(Given)
By, using Side-Side-Side (SSS Rule), we can write:
As the triangles are congruent, the angles should be of equal measurement.
Therefore, [Using Corresponding parts of the congruent triangle (CPCT)]
Hence, the above theorem is proved.
Theorem 2 : If the angles subtended by the chords of a circle at the centre are equal, then the chords are equal.