हमे ज्ञात है कि वृत्त के व्यास के अतिरिक्त किसी जीवा के अंतिम बिंदु उसे दो चापों में विभाजित करते हैं, जिन्हें दीर्घ चाप और लघु चाप कहते हैं। इस लेख में हम वृत्त के चाप द्वारा अंतरित कोण से संबंधित प्रमेय और उसके पूर्ण स्पष्टीकरण के साथ उसके प्रमाण पर चर्चा करेंगे।
एक वृत्त के चाप द्वारा अंतरित कोण – प्रमेय एवं प्रमाण
प्रमेय:
एक चाप द्वारा केंद्र पर बनाया गया कोण वृत्त के शेष भाग पर किसी भी बिंदु पर बनाए गए कोण का दोगुना होता है।
प्रमाण:
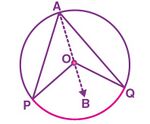
केंद्र  वाले एक वृत्त पर विचार करें। यहाँ वृत्त का चाप
वाले एक वृत्त पर विचार करें। यहाँ वृत्त का चाप  केंद्र
केंद्र  पर कोण
पर कोण  तथा वृत्त के शेष भाग पर स्थित बिंदु
तथा वृत्त के शेष भाग पर स्थित बिंदु  पर कोण
पर कोण  अंतरित करता है।
अंतरित करता है।
प्रमाण करने हेतु : 
इसे प्रमाणित करने के लिए,  को जोड़ें और इसे बिंदु
को जोड़ें और इसे बिंदु  तक विस्तारित करें
तक विस्तारित करें
इस प्रमेय को सिद्ध करते समय दो सामान्य स्थितियाँ हैं।
स्थिति 1:
Consider a triangle 
Here,  (Radii)
(Radii)
Since, the angles opposite to the equal sides are equal,

Also, by using the exterior angle property (exterior angle is the sum of interior opposite angles),
We can write,

By using 


Similarly, consider another triangle  ,
,
 (Radii)
(Radii)
As the angles opposite to the equal sides are equal,

Similarly, by using the exterior angle property, we get
 (using
(using  )
)

Adding  and
and  we get,
we get,



Hence, case (1) is proved.
Case 2:
To prove  for this case, we can follow the steps as same as for case
for this case, we can follow the steps as same as for case  . But while adding
. But while adding  and
and , we have to follow the below steps.
, we have to follow the below steps.

Reflex angle  (Since,
(Since,  is a Major arc)
is a Major arc)
Reflex angle  .
.
Hence, proved.