त्रिकोणमिति
Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the relationship between ratios of the sides of a right-angled triangle with its angles. The ratios used to study this relationship are called trigonometric ratios, namely, sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant. The word trigonometry is a 16th century Latin derivative and the concept was given by the Greek mathematician Hipparchus.
Introduction to Trigonometry
Trigonometry is one of the most important branches in mathematics. The word trigonometry is formed by clubbing words 'Trigonon' and 'Metron' which means triangle and measure respectively. It is the study of the relation between the sides and angles of a right-angled triangle. It thus helps in finding the measure of unknown dimensions of a right-angled triangle using formulas and identities based on this relationship.
Trigonometry Basics
Trigonometry basics deal with the measurement of angles and problems related to angles. There are three basic functions in trigonometry: sine, cosine, and tangent. These three basic ratios or functions can be used to derive other important trigonometric functions: cotangent, secant, and cosecant. All the important concepts covered under trigonometry are based on these functions. Hence, further, we need to learn these functions and their respective formulas at first to understand trigonometry.
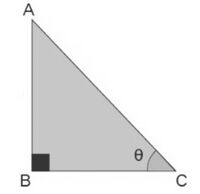
In a right-angled triangle, we have the following three sides.
Perpendicular - It is the side opposite to the angle .
Base - This is the adjacent side to the angle .
Hypotenuse - This is the side opposite to the right angle.
Trigonometric Ratios
There are basic six ratios in trigonometry that help in establishing a relationship between the ratio of sides of a right triangle with the angle. If is the angle in a right-angled triangle, formed between the base and hypotenuse, then
- = Perpendicular/Hypotenuse
- = Base/Hypotenuse
- = Perpendicular/Base
The value of the other three functions: depend on respectively as given below.
- = Base/Perpendicualr
- = Hypotenuse/Base
- = Hypotenuse/Perpendicular
गणित की वह शाखा है, जो एक समकोण त्रिभुज की भुजाओं और कोणों से संबंधित है। यह ग्रीक शब्द ‘त्रि’ से लिया गया है, जिसका अर्थ है तीन, ‘गॉन’ जिसका अर्थ है भुजाएं, ‘मेट्रोन’ का अर्थ है माप। इसका उपयोग आरंभ के खगोलविदों और मिस्र और बेबीलोन में किया गया था। इस इकाई में हम त्रिकोणमिति क्या है यह जानेंगे ।
त्रिकोणमिति का परिचय
विभिन्न कोणों (0 से 90 डिग्री) के लिए त्रिकोणमिति और त्रिकोणमितीय अनुपातों का प्रयोग करने के बाद इसका उपयोग आर्किटेक्चर, इंजीनियरिंग, भौतिक विज्ञान जैसे विषय में देख सकते हैं। त्रिकोणमिति गणित की वह शाखा है, जिसमें त्रिभुज की तीनों भुजाओं और तीनों कोणों का अध्ययन किया जाता है।त्रिकोणमिति का अर्थ त्रिभुज की तीनों भुजाओं का माप होता है।
त्रिकोणमिति की खोज
त्रिकोणमिति का आविष्कार और प्रयोग प्राचीन भारत में किया गया। त्रिकोणमिति के जनक, शून्य और दशमलव का महत्व बताने वाले विश्व के महान गणितज्ञ और खगोलशास्त्री आर्यभट् हैं।
त्रिकोणमिति का उपयोग
त्रिकोणमिति का उपयोग गणित, विज्ञान और तकनीकी में किया जाता है। त्रिकोणमिति के अध्ययन के बाद हम इसका उपयोग निम्न चीजों में देखते हैं-
- खेतों, भूखंडों और क्षेत्रों को मापना
- सिरेमिक टाइल की माप